surgical nerve repair for nerve compression
Nerves may be squeezed by surrounding tissues, which increases pressure on the nerve and may cause muscle weakness, a burning or tingling sensation, numbness or pain. Compression injuries are also common near joints such as the elbow, wrist, or ankle where the nerve might be compressed by the joint bones, ligaments, tendons or surrounding muscles.
how is compression repaired?
Think of nerve compression like a kink in a garden hose. In a compression injury, tissue pinches the nerve, preventing the signal from getting through. Cutting or removing the tissue restricting the nerve allows the nerve to heal and restore normal signal transmission. After releasing the nerve, the surgeon may decide to protect the nerve by placing fat around it, wrapping the nerve with vein tissue or using a nerve protector.

what causes compression?
Carpal or cubital tunnel are examples of nerve compression that occur when pressure is applied to a nerve by surrounding tissues, such as bones, cartilage, ligaments, tendons or muscles. This pressure disrupts the nerve’s function, causing pain, tingling, numbness or weakness. Learn more

could I have nerve damage?
Explore how nerve damage can happen and learn about how different nerves work throughout the body.
Your doctor will provide recommendations, but read on to learn about various repair options for different types of nerve damage.
for compressed nerves
nerve wraps
A nerve wrap protects the injured nerve during the healing process, acting as a barrier to protect the nerve from the surrounding tissue.

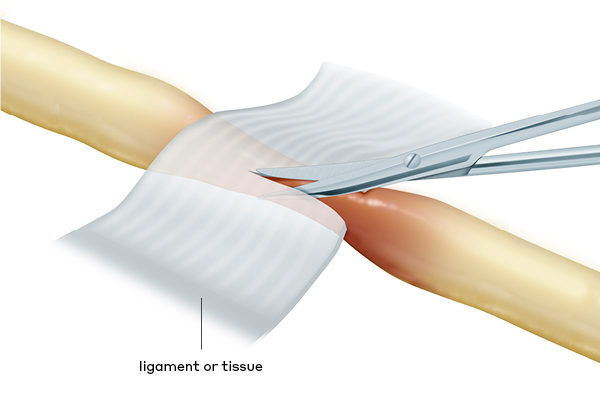
nerve release
A surgical procedure to relieve pressure on the entrapped nerve by cutting ligament(s) or tissue attachments surrounding the nerve. An example is the procedure to cut the transverse carpal ligament in patients with carpal tunnel syndrome.
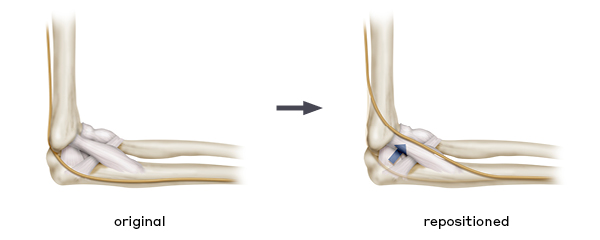
nerve repositioning (transpositioning)
A surgical procedure to slightly reposition the nerve to move it out of the way of an implant or natural anatomic obstruction to prevent it from being compressed. An example is the procedure to move the nerve to a different position in patients with cubital tunnel syndrome.
healthy peripheral nerves allow us to

